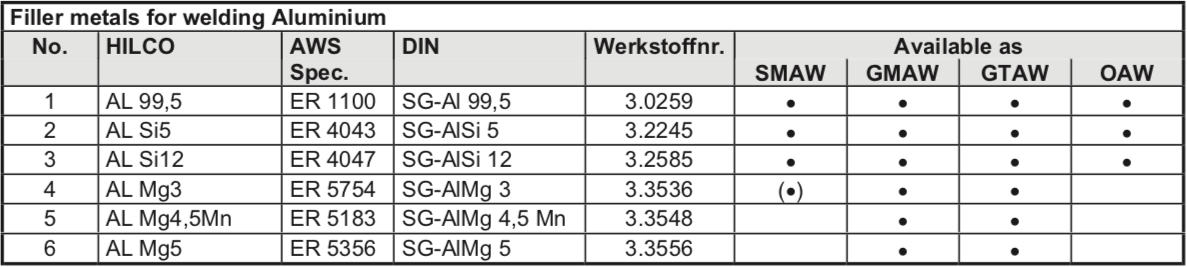
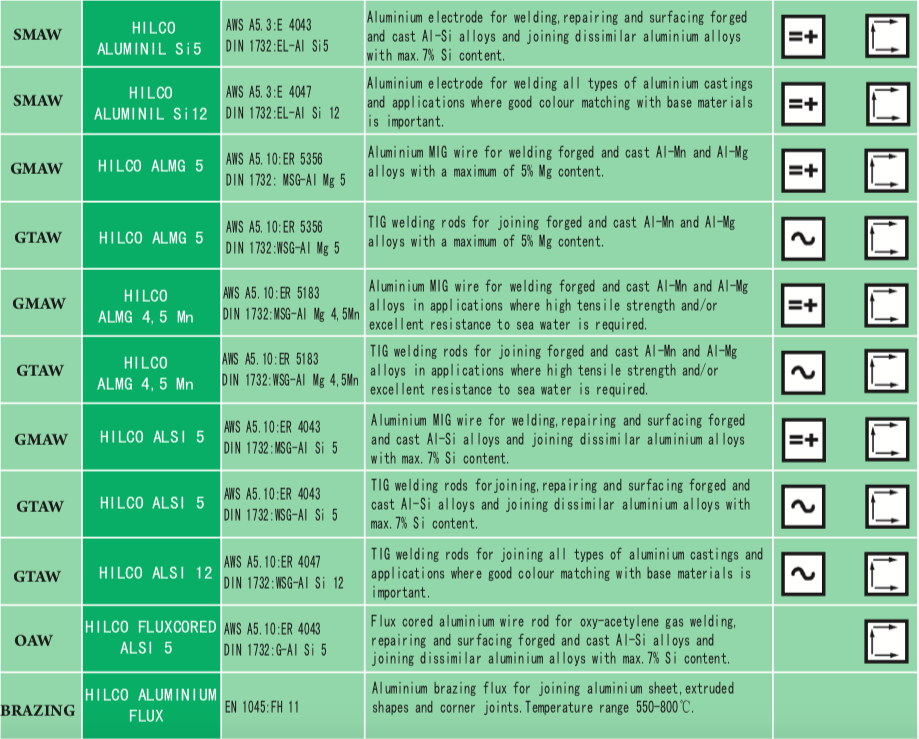
Hilco Product info
HILCO – P2
“Flying without wings” with HILCO Aluminium welding wires!”
Hilco Product infoHaarlem, 30th of June 2005 – Holland is working, together with Belgium, on boundless transport. From the year 2007 the HSL(high speed line) will connect Amsterdam with Antwerp and Brusselswith Paris. Connection to the Europea net of high speed lines makes travelling through Europeeasier and offers above all an environment friendly alternative for travelling by car and plane.It isexpected that many travellers will use the “flying without wings” in the future.
High speed trains will travel with a maximum speed of 300 km per hour over the HSL-South Line. These speeds require optimum performance, guaranteed safety and confidence. So it is not remarkable to see that for the construction it has been chosen for Aluminium in most cases. By its specific characteristics aluminium offers an ideal combination of optimum strength and a low weight.
Like always, specific demands require specific treatment. With aluminium wires the surface is crucial: it must be absolutely clean in order to avoid problems like porosity. During production, the wires are treated in a special way called “shaving”. By repeating this twice and immediately after “polishing”, all pollution is removed. With this treatment we guarantee you a problem free application of our Hilco wires in your aluminium welding process.

Welding of Aluminium
Aluminium is successfully welded only after careful thought and preparation. Through correct preparation, it is easier to avoid the pitfalls that can trap the unwary. Therefore this introduction with facts on base metals, welding methods, types of joint and filler metals. This introduction is just a general guideline, please contact us for more information.
Base metals
Aluminium and its alloys can be divided into three major groups:
• Aluminium
• Nonhardenable / non heat treatable alloys
• Hardenable / heat treatable alloys
Aluminium is developed in various grades of purity. The most common commercial grades contain 99,7-99,5 or 99,0% aluminium. Non-hardenable alloys, i.e. not suitable for heat treatment, contain small amounts of Mn or Mg. AlMn alloys are often made up of between 1,0-1,2%Mn, while AlMg alloys with up to 5% are quite common. AlMgMn alloys are also used. The hardenable alloys contain copper (Cu), magnesium and silicon (Mg+Si), or zinc and magnesium (Zn+Mg).
Aluminium and most of the non-heat treatable and heat treatable alloys possess good weldability. In the case of hardenable alloys with copper and lead additives, there is a risk of hot cracking and there fore they are difficult-to-weld. Many casting alloys are also suitable for welding except in the case of those, which have high content of copper or magnesium which cannot be welded.


|
Welding application
|
Special considerations
|
Common base materials
|
Filler metal selection
|
|
Shipbuilding and sub suppliers Requirements: Saltwater corrosion resistance, pressure vessel service, thick plate welding
|
|||
|
Structural frames
|
Strength & fatigue, corrosion, extrusions & cut plate
|
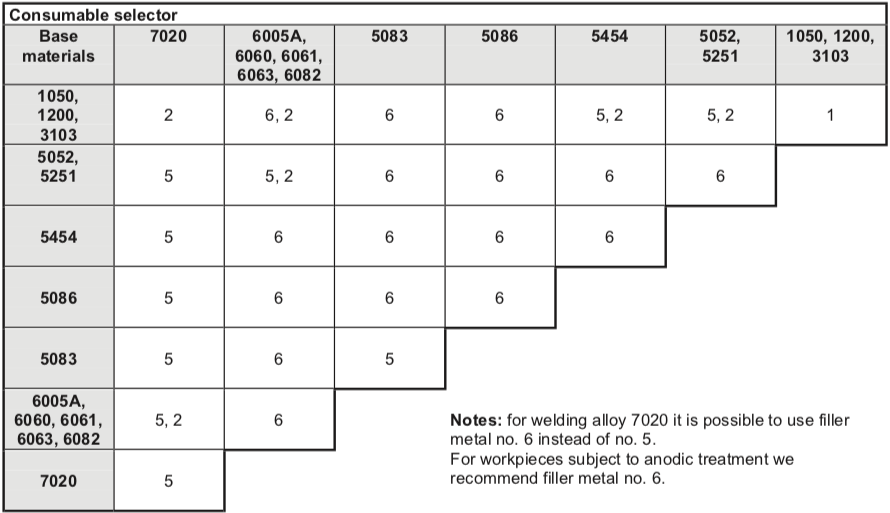
6061 to 6061
6061 to 5086
5086 to 5086
5083 to 5083
|
AL Mg5 AL Mg5 AL Mg5 AL Mg4,5Mn
|
|
Skin
|
Strength & corrosion
|
5052 to 5052
5086 to 5086
6061 to 6061
5083 to 5083
|
AL Mg5, AL Si5 (2nd choice) AL Mg5 AL Mg5 AL Mg4,5Mn
|
|
Desalination units
|
Corrosion & high temperatures
|
5454 to 5454
5052 to 5052
|
AL Mg3 AL Mg3
|
|
Tube railings
|
Strength & anodize
|
6061 to 6061
6063 to 6063
|
ÁL Mg5 AL Mg5
|
|
Structural plate & LNG tanks
|
Impact strength & cold temperature properties
|
5083 to 5083
|
AL Mg4,5Mn
|
|
Marine cast hardware
|
Strength & corrosion
|
5180 to 5180
5350 to 5350
|
AL Mg5 AL Mg5
|
|
Cars, manufacturing and sub suppliers Requirements: Thin wall brazing for heat exchangers, corrosion resistant high strength wheels, high torque drive components, body and frame joining
|
|||
|
Heat exchangers
|
Pressure seal, corrosion resistance & thin wall burst pressure
|
3003 to 3003
3003 to 6061
6061 to 6061
|
AL Si12, AL Si5 (2nd choice) AL Si12, AL Si5 (2nd choice) AL Si12, AL Si5 (2nd choice)
|
|
Wheels
|
Shear strength, fatigue and high temperature
|
5454 to 5454
5454 to 6061
5356 to 5454
|
AL Mg3 AL Mg3 AL Mg3
|
|
Drive shafts
|
Torque / shear strength & fatigue
|
6061 to 6061
|
AL Mg5
|
|
Bumpers & supports
|
Impact strength, corrosion resistance & extrusions
|
7005 to 7005
7029 to 7029
|
AL Mg5
|
|
Body panels
|
Tensile strength, corrosion resistance & thin wall welding
|
6009 to 6009
6011 to 6011
|
AL Si5, ALSi 12 (2nd choice) AL Si5, ALSi 12 (2nd choice)
|
|
Frame sections
|
Strength & fatigue
|
6061 to 6061
|
AL Si5
|
|
Trucks, buses and trailers Requirements: High quality production welding technology, product cost optimation, product reliability engineering
|
|||
|
Formed truck panels
|
Formability & corrosion resistance
|
5052 to 5052
5052 to 5454
5454 to 5454
|
AL Mg5 AL Mg5 AL Mg5
|
|
Engine blocks cast housings
|
Weld cracking
|
356 to 356
|
AL Si12
|
|
Cylinder heads
|
Weld cracking
|
A201.0 to A201.0
240.0 to 240.0 242.0 to 242.0
|
AL Si12 AL Si12 AL Si12
|
|
Forged pistons
|
Weld cracking
|
2218 to 2218 2618 to 2618
|
AL Si5 AL Si5
|
|
Welding application |
Special considerations |
Common base materials |
Filler metal selection |
|
Trucks, buses and trailers |
|||
|
Truck panels |
Strength, cost efficiency & fatigue |
5454 to 5454 |
AL Mg5, AL Mg3 (2nd choice) AL Mg5 AL Mg5, nd AL Mg4,5Mn (2 choice) |
|
Chemical tankers |
Strength & corrosion resistance |
5254 to 5254 |
AL Mg4,5Mn |
|
Line heaters & steam liners |
Strength & high temperature |
5454 to 5454 |
AL Mg3 |
|
Trim |
Formability, anodise & polish |
5050 to 5050 |
AL Mg5 AL Mg5 |
|
Trains, railway cars |
|||
|
Train panels |
Strength & fatigue cost efficiency |
5454 to 5454 5086 to 5086 5083 to 5083 |
AL Mg5, AL Mg3 (2nd choice) AL Mg5 |
|
Aerospace & defence industry |
|||
|
Aerospace hardware |
Strength-to-weight ratio |
6061 to 6061 6013 to 6013 If anodised PWHT |
AL Si5 AL Si5 AL Mg5 AL Si5 |
|
Turbine blades and torque converters |
Strength-to-weight ratio |
711.0 to 711.0 |
AL Mg5 |
|
Armour plate |
Impact strength & strength-to- weight ratio |
5083 to 5083 7039 to 7039 |
AL Mg5 AL Mg5 |
|
Military bridges |
Strength-to-weight ratio |
7039 to 7039 PWHT |
AL Mg5 |
|
Other transport equipment |
|||
|
Bicycle frames & sport wheels |
Strength fatigue & anodise |
6061 to 6061 6061 to 6061 PWHT 7005 to 7005 7046 to 7046 5086 to 5086 |
AL Mg5 AL Si5 AL Mg5, nd AL Mg4,5Mn (2 AL Mg5, ndAL Mg4,5Mn (2 AL Mg5 choice) choice) |
|
Tops & sleds |
Deep drawing & forming |
1100 to 1100 1100 to 1100 |
AL 99,5 AL Si5 |
|
Frame extrusions & body sheet |
Strength-to-weight ratio & forming |
6061 to 6061 5454 to 5454 5086 to 5086 5052 to 5052 |
AL Mg5 AL Mg5 AL Mg5 AL Mg5 |
|
Welding application |
Special considerations |
Common base materials |
Filler metal selection |
|
Energy generation incl. boilers and pressure vessels. Turbines. power plants, windmills |
|||
|
Pressure vessel |
Strength |
5456 to 5456 |
AL Mg4,5Mn |
|
Marine & cryogenic tanks |
Temperature & strength |
5083 to 5083 |
AL Mg4,5Mn |
|
Chemical tanks |
Chemical (acids), processing (food), H2O2, corrosion & strength |
1060 to 1060 1100 to 1100 3003 to 3003 5254 to 5254 |
AL Si5 AL Si5 AL Si5 AL Mg3 |
|
General repair & maintenance |
|||
|
General repairs of aluminium products e.g. cylinders heads, machine bases, small engine crank cases, marine etc. |
Pure/cast Al anodised, |
N/A N/A 6060 / 6083 N/A N/A |
AL 99,5 Aluminil 99,5 AL Mg3 Aluminil Mn1 Aluminil Si12 Aluminil Si5 |
